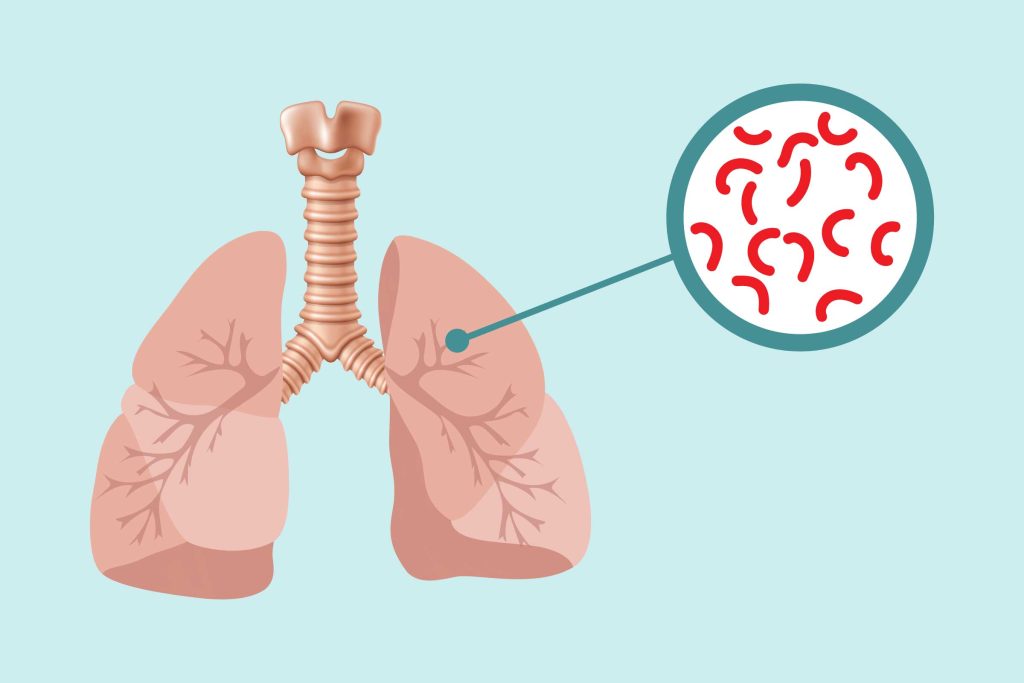
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious infection caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It mainly affects the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body. TB spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Symptoms include a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. TB is treatable and curable with antibiotics taken over several months.
Types:
- Latent TB Infection (LTBI):
- Bacteria are in the body but inactive.
- No symptoms.
- Not contagious.
- Can become active later, so treatment is still important.
- Active TB Disease:
- Bacteria are active and multiplying.
- Causes symptoms and is contagious.
- Requires immediate treatment.
Symptoms of Active TB (Pulmonary):
- Persistent cough (lasting more than 3 weeks)
- Coughing up blood or sputum
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
Cause:
- Caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Spread through the air when a person with active TB coughs, sneezes, or talks.
Treatment for tuberculosis depends on whether the infection is latent or active, and whether the TB strain is drug-sensitive or drug-resistant.
1. Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Treatment
Latent TB means the bacteria are present in the body but inactive. There’s no illness or contagiousness, but treatment is essential to prevent progression to active TB.
Common Treatment Options:
- Isoniazid (INH) for 6–9 months
- Rifampin for 4 months
- Isoniazid + Rifapentine once weekly for 3 months
- (known as 3HP regimen, usually DOT—Directly Observed Therapy)
2. Active TB Disease Treatment
Active TB means the bacteria are multiplying and causing illness. Treatment must begin immediately and be strictly followed.
First-Line Anti-TB Drugs (Standard 4-Drug Regimen):
- Isoniazid (INH)
- Rifampin (RIF)
- Pyrazinamide (PZA)
- Ethambutol (EMB)