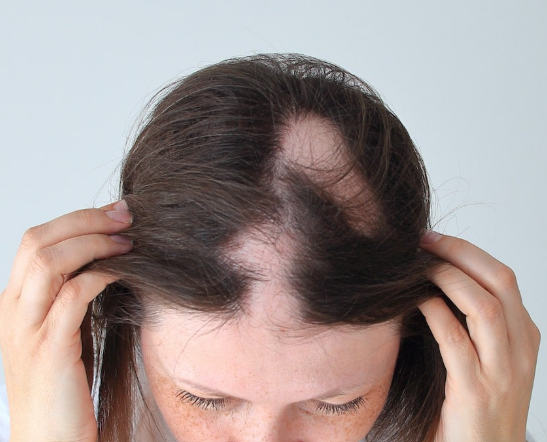
Pelade is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to localized bald patches on the scalp, beard, eyebrows, or other hair-bearing areas.

Causes of Pelade:
1. Autoimmune Reaction
- The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles, treating them as foreign.
- This stops hair growth temporarily, causing bald patches.
2. Genetic Factors
- Family history increases the risk.
- About 10–20% of patients have relatives with alopecia areata or other autoimmune diseases.
3. Other Autoimmune Conditions
People with pelade are more likely to have or develop:
- Thyroid disease (Hashimoto, Graves)
- Vitiligo
- Type 1 diabetes
- Rheumatoid arthritis
4. Environmental Triggers
- Stress (physical or emotional)
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Hormonal changes
5. Genetic & Immune System Interaction
- Certain genes (HLA types) increase susceptibility.
- Triggering factors (like stress or infection) can activate the immune attack in genetically predisposed people.
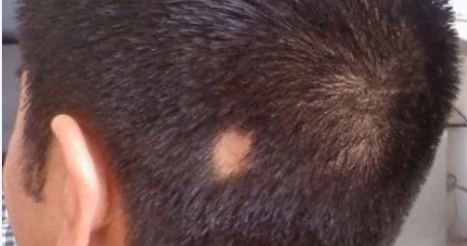
symptoms of Pelade:
1. Hair Loss (most common sign)
- Sudden appearance of round or oval bald patches on the scalp, beard, eyebrows, eyelashes, or other body areas.
- The skin in bald patches looks smooth, normal, and not scarred.
2. Exclamation Mark Hairs
- Short broken hairs that are narrower at the base (like an exclamation mark), often seen at the edge of bald patches.
3. Changes in Nails (in some patients)
- Tiny pits (small depressions) on the nail surface.
- Ridges or roughness of nails.
- Nails may become thin, brittle, or split.
4. Pattern of Hair Loss
- May stay limited to small patches.
- Can progress to:
- Alopecia totalis → complete scalp hair loss.
- Alopecia universalis → loss of all body hair.
5. Other Features
- Usually no itching or pain.
- Sometimes mild tingling or burning sensation before hair falls.
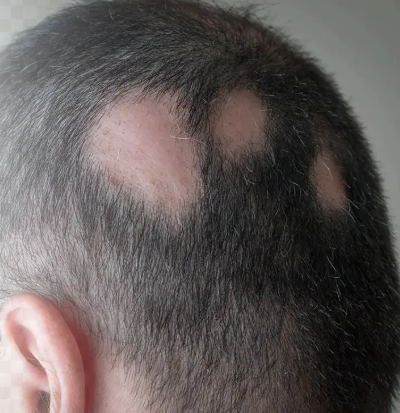
Treatment for Pelade ( Alopecia Areata):
1. Topical Treatments (applied on skin)
- Corticosteroid creams or ointments → reduce immune attack on hair follicles.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine®) → stimulates hair growth.
- Topical immunotherapy (DPCP, SADBE) → creates mild allergic reaction to distract immune system from attacking follicles.
- Anthralin cream → alters immune activity in the skin.
2. Injections
- Corticosteroid injections directly into bald patches (common for small areas).
- Helps hair regrow within weeks to months.
3. Oral Medications (for severe cases)
- Corticosteroid tablets → short-term use (risk of side effects).
- Immunosuppressants: methotrexate, cyclosporine, azathioprine.
- JAK inhibitors (new treatments): tofacitinib, baricitinib, ruxolitinib → promising results in resistant cases.
4. Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
- UV light treatment (PUVA) sometimes used.
5. Supportive Measures
- Wigs, hairpieces, scarves for cosmetic cover.
- Psychological support (stress management, counseling).
- Balanced diet, reducing stress, treating underlying autoimmune disease.