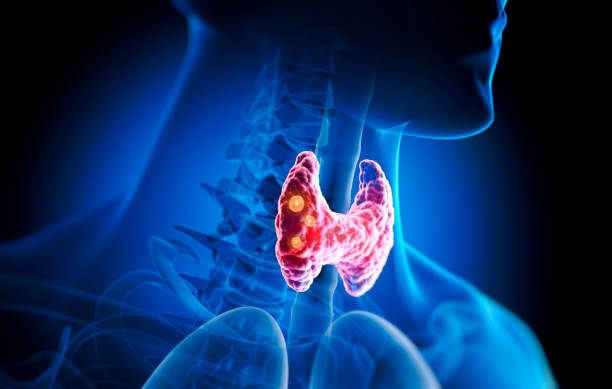
Goiter is the abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland in the neck, usually caused by iodine deficiency or thyroid dysfunction, which can affect hormone production and may lead to swelling, difficulty swallowing, or breathing problems.
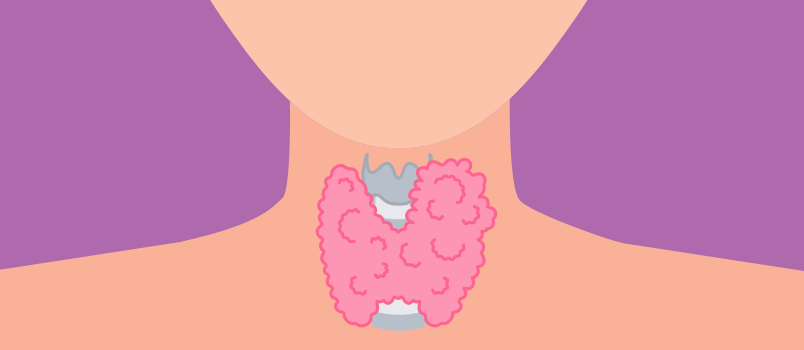
Causes
- Iodine deficiency (most common worldwide) – the thyroid enlarges in an attempt to trap more iodine to make thyroid hormones.
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) – e.g., Graves’ disease.
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) – e.g., Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Thyroid nodules or cancer.
- Certain medications (like lithium).
Symptoms:
- Visible & Physical Signs
Swelling at the base of the neck (may be symmetrical or one-sided).
Tightness or fullness in the throat.
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
Difficulty breathing (if the goiter presses on the windpipe).
Hoarseness or voice changes (if the goiter presses on vocal cords). - Symptoms Related to Thyroid Function Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid):
Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, constipation, hair loss, slow heart rate.
Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid):
Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, tremors, heat intolerance, sweating, irritability.
treatment:
1. Iodine Deficiency Goiter
- Supplementation with iodine (iodized salt or iodine tablets).
- Ensures proper thyroid hormone production.
2. Hyperthyroid or Hypothyroid Goiter
- Hyperthyroid (overactive thyroid):
- Anti-thyroid medications (e.g., methimazole).
- Radioactive iodine therapy in some cases.
- Hypothyroid (underactive thyroid):
- Thyroid hormone replacement (e.g., levothyroxine).
3. Large or Symptomatic Goiter
- Surgery (thyroidectomy) if the goiter causes breathing or swallowing problems, or if there’s suspicion of cancer.
4. Lifestyle & Monitoring
- Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels.
- Avoiding goitrogenic foods in large amounts (like raw cabbage or soy) if sensitive.