Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by high blood glucose (blood sugar) levels due to problems with insulin production, function, or both.

Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes
- Cause: Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Onset: Usually in childhood or adolescence, but can occur at any age.
- Treatment: Requires lifelong insulin therapy.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
- Cause: Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency.
- Onset: More common in adults over 40, but increasingly seen in children.
- Risk factors: Obesity, sedentary lifestyle, genetics, poor diet.
- Treatment: Lifestyle changes, oral medications (e.g., metformin), and possibly insulin.
3. Gestational Diabetes
- Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after delivery.
- Increases risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
4. Other Specific Types
- Due to genetic mutations, pancreatic diseases, or certain medications (e.g., steroids).
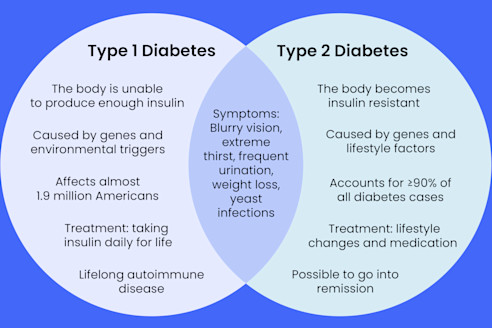
Symptoms of Diabetes
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Increased hunger
- Slow-healing wounds
- Numbness or tingling (especially in hands/feet)
Some people with type 2 diabetes may have mild or no symptoms for years.

Management and Treatment
Lifestyle Changes (essential for all types)
- Healthy diet: Low in simple sugars, balanced carbs, high fiber
- Regular exercise: Improves insulin sensitivity
- Weight control: Even 5–10% weight loss can have big impact
Medications
For Type 2 Diabetes:
- Metformin – First-line medication
- SGLT2 inhibitors – Help the kidneys excrete sugar
- GLP-1 receptor agonists – Enhance insulin secretion and satiety
- Sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, etc.
- Insulin – Required if oral drugs aren’t enough
For Type 1 Diabetes:
- Insulin (essential):
- Basal (long-acting)
- Bolus (short-acting or rapid-acting)