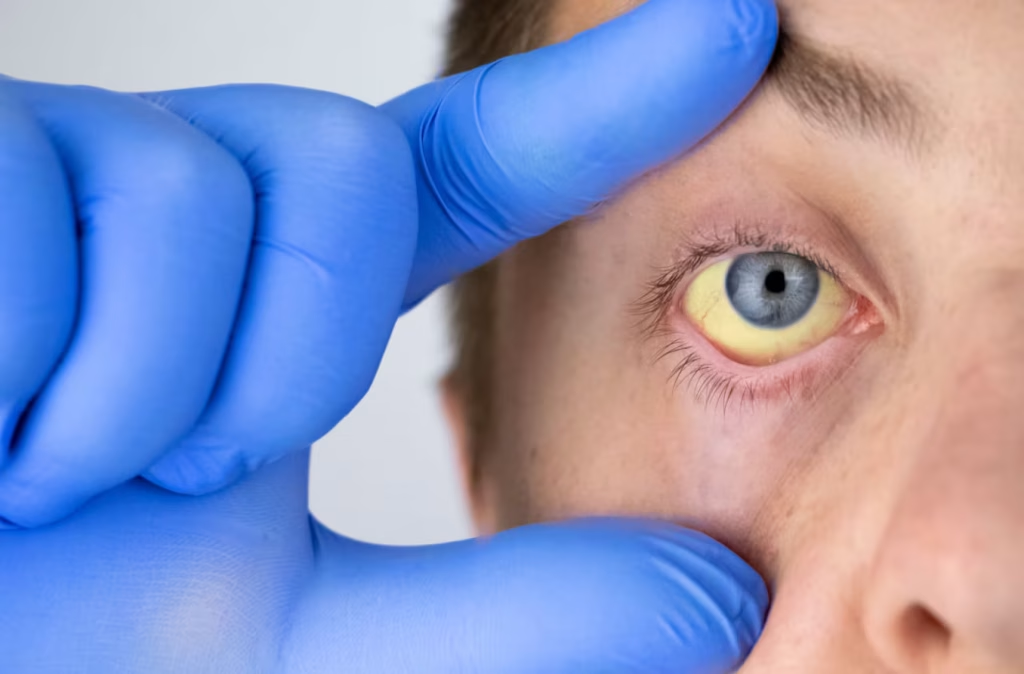
Anemia is a condition where your body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to your tissues.
Anemia symptoms depend on its severity and how quickly it develops. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Cold hands and feet
- Chest pain or irregular heartbeat
- Headache
- Poor concentration
- Brittle nails or hair loss
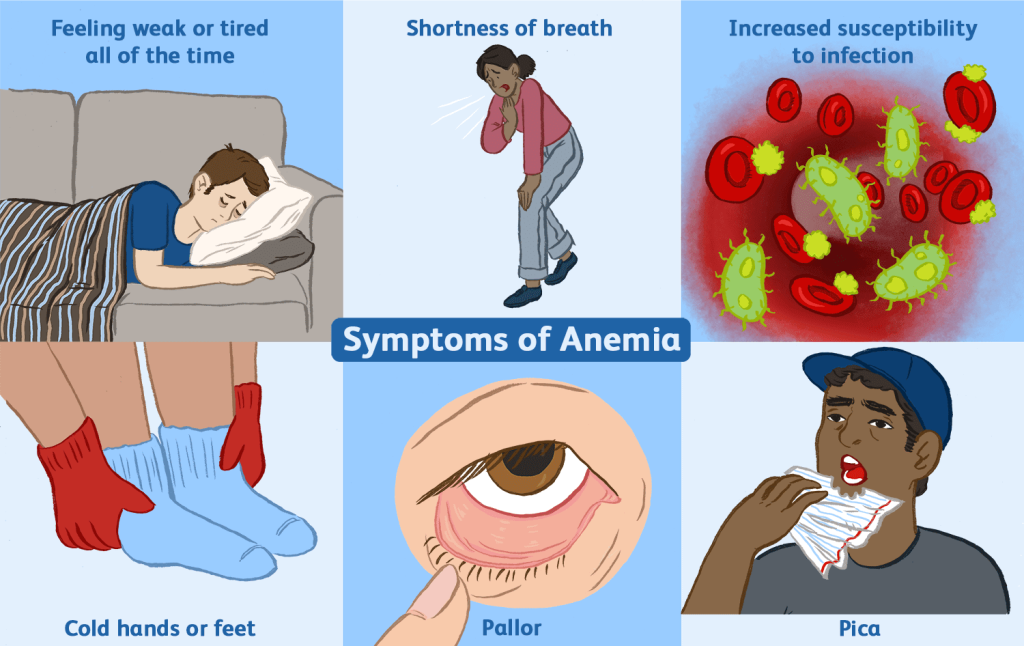
Anemia symptoms often start with fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. As it worsens, you might feel short of breath, dizzy, or experience a rapid heartbeat. Other signs can include cold hands and feet, headaches, brittle nails, or unusual cravings like ice (pica). Some types, like B12 deficiency, may also cause tingling in the hands or memory issues. If severe, anemia can lead to chest pain or fainting.
Anemia is treated with iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid supplements, depending on the cause. In severe cases, blood transfusions or treatment of underlying conditions may be needed.

Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Vitamin B12 injections (e.g., if due to pernicious anemia)
- Oral B12 supplements (for mild deficiency or dietary causes)
- Dietary sources: meat, eggs, dairy, fortified cereals
- Monitor for neurological symptoms (can be irreversible if untreated)
Here’s a simple diet plan for anemia that focuses on iron and nutrients that help red blood cell production:
1. Iron-Rich Foods
- Heme iron (best absorbed): red meat, chicken, turkey, liver, fish
- Non-heme iron: lentils, beans, tofu, spinach, pumpkin seeds, fortified cereals
2. Vitamin C (boosts iron absorption)
- Oranges, strawberries, tomatoes, bell peppers, broccoli, kiwi
3. Folic Acid Sources
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale), avocados, legumes, fortified grains
4. Vitamin B12 Sources
- Eggs, dairy, meat, fish, fortified plant milks or cereals (for vegetarians/vegans)
I was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease four years ago. For over two years, I relied on prescription medications and therapies, but unfortunately, the symptoms continued to worsen. My mobility declined, tremors increased, and I experienced growing fatigue and discomfort that affected my daily life. Last year, out of desperation and hope, I decided to try an herbal treatment program from NaturePath Herbal Clinic. Honestly, I was skeptical at first, but within a few months of starting the treatment, I began to notice real changes. My energy improved, the discomfort eased, and I felt stronger and more capable in my daily life. Incredibly, I also regained much of my stamina, balance, and confidence. It’s been a life-changing experience I feel more like myself again, better than I’ve felt in years. If you or a loved one is struggling with Parkinson’s disease, I truly recommend looking into their natural approach. You can visit their website at http://www.naturepathherbalclinic.com