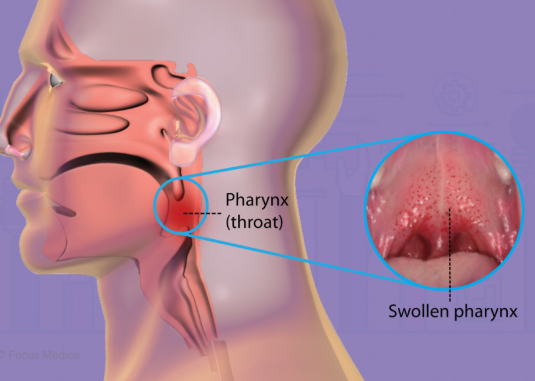
Pharyngitis is the medical term for inflammation of the pharynx, the part of the throat located behind the mouth and nasal cavity. It is most commonly experienced as a sore throat, often accompanied by pain or discomfort when swallowing, redness, and sometimes fever or swollen tonsils.
The causes of Pharyngitis:
1. Infectious causes
- Viral infections (most common, ~70–90% of cases):
- Common cold viruses (rhinovirus, coronavirus, adenovirus)
- Influenza virus
- Epstein–Barr virus (mononucleosis)
- Herpes simplex virus
- Bacterial infections (less common, but important to recognize):
- Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A streptococcus) → causes strep throat
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrheal pharyngitis)
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae (diphtheria, rare in vaccinated populations)
2. Non-infectious causes
- Allergies (pollen, dust, pet dander)
- Dry air or dehydration
- Smoking and secondhand smoke
- Air pollution and chemical irritants
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), where stomach acid irritates the throat
- Excessive voice use (shouting, singing)
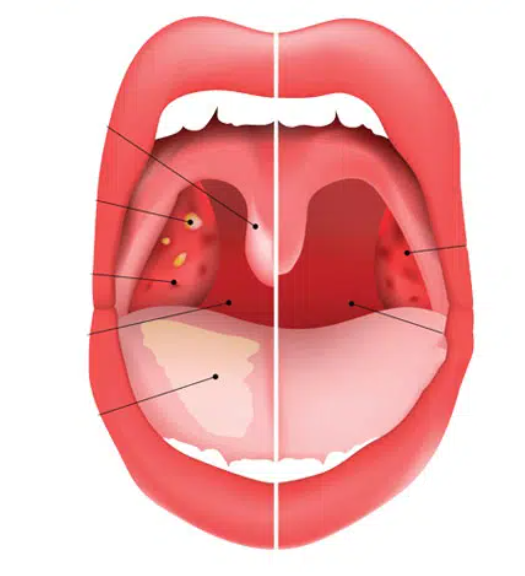
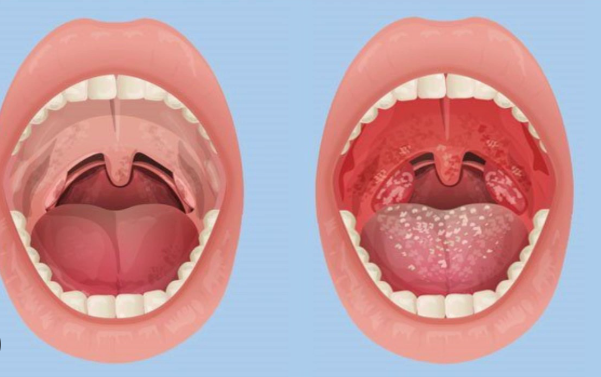
the symptom of Pharyngitis:
The main symptom of pharyngitis is a sore throat, which is often described as pain, irritation, or a scratchy sensation in the throat, especially when swallowing. Other common symptoms may include redness of the throat, difficulty or pain while swallowing (odynophagia), swollen tonsils, and sometimes white patches or pus on the tonsils in bacterial cases like strep throat. Additional symptoms can vary depending on the cause: viral pharyngitis may be accompanied by runny nose, cough, hoarseness, or conjunctivitis, while bacterial pharyngitis may present with sudden severe throat pain, fever, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, and absence of cough. In some cases, patients may also experience headache, fatigue, or body aches.
The treatment of pharyngitis
1. Home Care
- Avoid irritants: Stay away from smoke, alcohol, very spicy, or acidic foods.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of warm fluids (herbal teas, broths).
- Humidify the air: Use a humidifier to keep the throat moist.
- Saltwater gargle: Mix 1 tsp salt in 1 cup warm water; gargle several times daily.
- Rest your voice: Avoid yelling or excessive talking to reduce throat strain.
2. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
- Lozenges and throat sprays: Containing benzocaine or menthol to relieve pain.
- Pain relievers: Acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce discomfort and fever.
- Soothing remedies: Honey (not for children under 1 year) and warm teas for throat relief.
3. Prescription Treatments (for bacterial or severe cases)
- Antibiotics: Prescribed only if pharyngitis is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (strep throat).
- Corticosteroids: Occasionally used in severe throat swelling to reduce inflammation.
- Other medications: Depending on the cause, such as antivirals (rarely needed).
4. Address Underlying Causes
- Allergy management: Antihistamines or avoiding triggers if allergies are responsible.
- GERD treatment: Acid-reducing medications and lifestyle changes if reflux is the cause.
- Avoid irritants: Quit smoking and minimize exposure to pollutants or chemicals.
5. Pain Management
- Warm or cold fluids: Soups, teas, or ice chips can soothe throat pain.
- Soft foods: Yogurt, mashed potatoes, or smoothies to avoid further irritation.
- Rest: Adequate sleep supports immune recovery.