A stomach ulcer, also called a gastric ulcer, is a sore or open lesion that develops in the lining of the stomach when the protective mucus layer is weakened and stomach acid damages the tissue beneath.
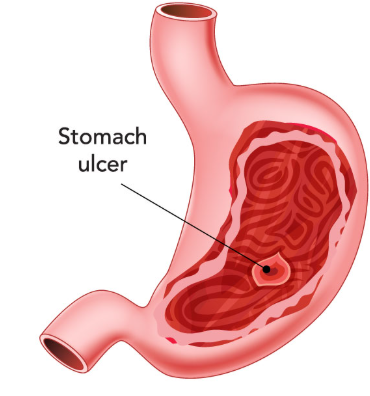
The causes of stomach ulcers
1. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection
- A common bacteria that lives in the stomach.
- Weakens the protective mucus layer → stomach acid damages the lining → ulcer formation.
2. Long-term use of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Examples: ibuprofen, aspirin, naproxen.
- These reduce protective stomach mucus and increase acid irritation.
3. Excess stomach acid production
- Can be triggered by stress, smoking, alcohol, spicy foods, or certain medical conditions (like Zollinger–Ellison syndrome).
The symptoms of a stomach ulcer:
Typical Symptoms
- Burning or gnawing pain in the upper abdomen (often between the chest and belly button).
- Pain that may get worse on an empty stomach and improve after eating or drinking milk.
- Bloating or feeling full quickly.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Loss of appetite and sometimes weight loss.
- Indigestion, belching, or heartburn.
Serious Symptoms (Need Urgent Care)
- Vomiting blood (red or coffee-ground appearance).
- Black, tarry stools (sign of bleeding).
- Sudden, severe abdominal pain (may mean perforation/rupture).
- Fainting, weakness, or paleness (possible anemia or internal bleeding).
Treatment of Stomach Ulcers:
1. Medications
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) – reduce acid, promote healing
- Examples: omeprazole, pantoprazole, esomeprazole
- H2-receptor blockers – lower acid production
- Examples: ranitidine, famotidine
- Antacids & protective agents – coat stomach lining
- Examples: sucralfate, bismuth subsalicylate
- Antibiotics (if H. pylori infection present) – usually a combination of 2 antibiotics + a PPI
- Example: clarithromycin + amoxicillin/metronidazole + PPI
2. Lifestyle & Self-care
- Avoid NSAIDs (ibuprofen, aspirin, naproxen) unless prescribed and protected by a PPI.
- Stop smoking and reduce alcohol intake.
- Limit spicy, acidic, and fried foods if they worsen symptoms.
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals.
- Reduce stress (stress doesn’t cause ulcers but can worsen healing).
3. Surgical Treatment (rare, for complications)
- Required if ulcer bleeds heavily, perforates, or blocks the stomach outlet.