Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the airways that carry air to and from the lungs. This condition causes the lining of the bronchial tubes to become irritated and swollen, leading to symptoms such as persistent coughing, mucus (phlegm) production, chest discomfort, wheezing, and sometimes shortness of breath.
There are two main types:
- Acute bronchitis – Usually caused by a viral infection (like the common cold) and lasts for a few days to a few weeks. It’s common and often resolves without serious complications.
- Chronic bronchitis – A long-term condition often caused by smoking or long-term exposure to irritants (like air pollution or chemical fumes). It’s a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and is characterized by a productive cough lasting at least 3 months in 2 consecutive years.
Treatment depends on the type and severity but may include rest, fluids, inhalers, or medications to ease symptoms and clear the airways. Avoiding smoking and irritants is key to prevention and management.
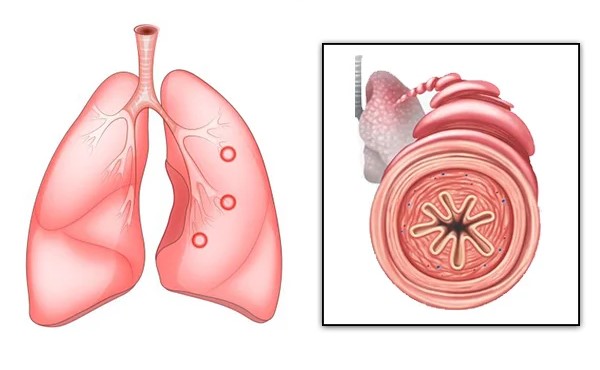
Causes :
Bronchitis can be caused by a variety of factors, depending on whether it is acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis is most commonly caused by viral infections, such as the common cold or influenza, and occasionally by bacterial infections. It can also be triggered by exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke, air pollution, dust, or chemical fumes. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is usually the result of long-term exposure to lung irritants. The most common cause is smoking, but repeated exposure to air pollution, industrial fumes, or secondhand smoke can also contribute. People who experience frequent respiratory infections are at higher risk of developing chronic bronchitis over time.
Causes of Bronchitis
Acute Bronchitis
- Viral infections (e.g., cold or flu viruses) – most common
- Bacterial infections – less common
- Irritants such as:
- Cigarette smoke
- Air pollution
- Dust
- Chemical fumes
Chronic Bronchitis
- Smoking – main cause
- Long-term exposure to:
- Air pollution
- Industrial or chemical fumes
- Dust or toxic gases
- Repeated respiratory infections
- Secondhand smoke exposure

Common Symptoms:
- Persistent cough
- Mucus production
- Wheezing
- Fatigue
- Chest tightness
- Mild fever (more in acute bronchitis)
Solutions for Bronchitis :
Bronchitis can be frustrating — that persistent cough, chest tightness, and fatigue can really wear you down. The good news? There are several effective solutions depending on whether it’s acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). Here’s a breakdown:
Acute Bronchitis
- Rest – to help the body recover
- Stay hydrated – drink plenty of fluids
- Over-the-counter medications:
- Pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen) for fever or discomfort
- Cough suppressants (if the cough is severe or disturbing sleep)
- Expectorants – to loosen mucus
- Humidifier or steam inhalation – to ease breathing
- Avoid irritants (e.g., smoking, pollution)
- Antibiotics – only if a bacterial infection is confirmed (most cases are viral)
Chronic Bronchitis
- Quit smoking – the most important step
- Avoid lung irritants – dust, fumes, pollution
- Bronchodilators – inhalers to open airways
- Steroid inhalers – to reduce inflammation
- Pulmonary rehabilitation – breathing exercises and physical therapy
- Oxygen therapy – in severe cases
- Regular vaccinations – flu and pneumonia vaccines to prevent infections