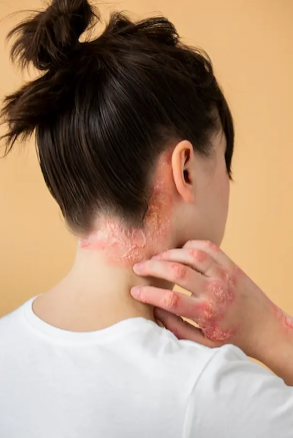
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder in which the immune system causes skin cells to grow too quickly, leading to thick, red, scaly patches on the skin.
- It is non-contagious.
- The condition often flares up periodically and may be triggered by stress, infections, or certain medications.
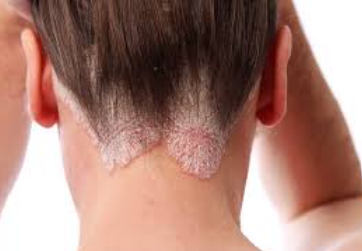
the causes of psoriasis:
1. Genetic Factors
- Psoriasis often runs in families.
- Certain genes make a person more susceptible to developing the disease.
2. Immune System Dysfunction
- Overactive T-cells attack healthy skin cells by mistake.
- This triggers inflammation and rapid skin cell growth.
3. Triggers (Do Not Directly Cause, But Can Worsen Psoriasis)
- Stress → physical or emotional stress can trigger flare-ups.
- Infections → streptococcal throat infection can trigger guttate psoriasis.
- Skin injuries → cuts, burns, or sunburn can provoke lesions (Koebner phenomenon).
- Medications → beta-blockers, lithium, antimalarials.
- Weather → cold, dry climates may worsen symptoms.
- Lifestyle factors → alcohol, smoking, obesity.
Common Symptoms:
- Red, raised patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales
- Itching, burning, or soreness
- Cracked skin that may bleed
- Dry or thickened skin
- Nail changes
- Pitting (small dents in nails)
- Discoloration
- Thickened or crumbling nails
Commonly Affected Areas:
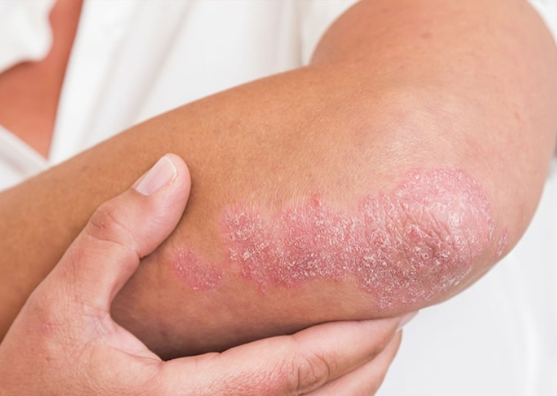
- Elbows and knees
- Scalp
- Lower back
- Face, palms, and soles
- Skin folds (especially in inverse psoriasis)
Types of Psoriasis and Specific Symptoms
- Plaque psoriasis → large, raised red patches with silvery scales (most common)
- Guttate psoriasis → small, drop-shaped red spots, often triggered by infection
- Inverse psoriasis → smooth red patches in skin folds (armpits, under breasts, groin)
- Pustular psoriasis → white pus-filled blisters on red skin
- Erythrodermic psoriasis → widespread redness and scaling, can be life-threatening
Treatment for psoriasis:
1. Topical Treatments (for mild to moderate psoriasis)
- Corticosteroid creams → reduce inflammation and itching
- Vitamin D analogs (e.g., calcipotriol) → slow skin cell growth
- Coal tar or salicylic acid preparations → reduce scaling and thickness
- Moisturizers → reduce dryness and irritation
2. Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
- Controlled exposure to UVB or PUVA light slows skin cell overproduction
- Often used when topical treatments are insufficient
3. Systemic Medications (for moderate to severe psoriasis)
- Methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin → suppress immune system to reduce inflammation
- Biologics (e.g., adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab) → target specific immune pathways involved in psoriasis
4. Lifestyle and Home Care
- Avoid triggers such as stress, infections, smoking, alcohol
- Maintain moisturized skin
- Gentle skin care to prevent irritation and injury
- Healthy diet and regular exercise may help reduce inflammation